TORNADO – Rapid Pre-cooling System for fresh crops.
PATENT SYSTEM
All fresh horticultural crops are living organisms, even after the harvest and they remain alive until they are consumed.
The necessary energy to continue this cycle of life is called respiraton.
During this phase the product produces heat raising the temperature and priming all the events of aging of the product.
The research confirms that lowering the respiration rate, as fast as possible, after harvest, is essential to preserve the quality of the fresh products.
A proper precooling preserves product quality by: inhibiting the growth of decay producing microorganisms, restricting enzymatic and respiratory activity, inhibiting water loss, and reducing ethylene production (Hardenburg et al. 1986 – note1).
The New " Tornado M-FAC1 System " (Mobil Forced Air Cooler - System)
Our firm has developed a new technology able to effectively answer to the problem of the rapid cooling: the " Tornado M-FAC1 System".
If compared to the other systems: the "Hidrocooling" or the “Vacum", the Forced Air cooling is one of the most economic methods that quickly remove the field heat.
Where is placed:
The System "MRP1" is used inside the most common cold rooms, with extreme simplicity.
What it does:
A powerful fan pulls the cold air from the cold room crossing the product, allowing to get a perfect cooling in rapid times - 1/3 in comparison to the common cold rooms where the product is simply positioned and slowly and not uniformly cooled, through a light contact with cold air.
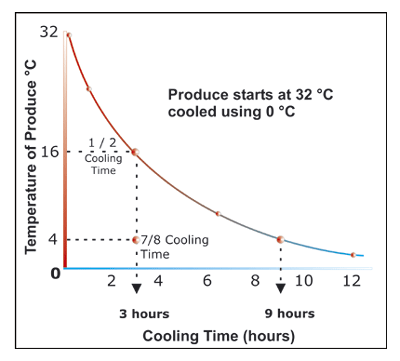 |
Example of Peaches loaded at 32°C inside a cold room:
Cooling Time inside a traditional cold room: 4°C in 9h (*) (*) Difference among the initial temperature (32°C) and the 7/8 of the same temperature and 3 times the ½ of the cooling time.
Cooling Time using M-FAC1 system: 4°C in 3h |
Source: Canada Plan Srervice - Tunnel Forced - Air Coolers.
Highly perishable products.
The cooling of the products through Forced Air is an easy application extensible to varied fresh horticultural crops. Nevertheless, some products have an higher intensity of respiration after harvest and, consequently, a notable water loss.
In the following chart some typologies of products are exemplified (note(3))
|
CLASS |
Co2 |
Cooling Time (h) |
Products |
|
HIGHEST - VI |
>60 |
0.75÷1.5 |
Asparagus, Broccolis, Mushrooms, Peas, Spinach, Indian Corn. |
|
VERY HIGH – V |
40-60 |
1÷2.5 |
Artichoke, String bean, Green Onions, Bruxelles cabbage. |
|
HIGH – IV |
20-40 |
2÷3.5 |
Stawberry, Bilberry, Raspberry, Cauliflower, Jackdaw. |
|
MEDIUM – III |
10-20 |
3÷4.5 |
Apricot, Banana, Cherry, Peach, Pear, Plum, Fig, Cabbage, Carrot, Lettuce, Peppers, Tomato, New Potato. |
|
LOW – II |
5-10 |
3.5÷5 |
Apples, Citrus, Grapes, Actinidia, Garlic, Onions, Potato. |
|
LOWEST - I |
<5 |
4÷6 |
Dattes, Dried fruits. |
(3)Source: A.A Kader 1985 – Criof g. Pratella, P. Bertolini –Cesena 30.04.1987
Note: Times changes beeing in relation to the entry temperature of the product, to the kind of pakging, to the cold plant and to other things.
The Advantages:
1) Rapid and homogeneous cooling on the whole product;
2) More resistances during the marketing;
3) More quality;
4) The system is adaptable for the most traditional and existing cold rooms;
5) The system in mobile and can be simply moved from a room to one other;
6) Energy saving, the system doesn't need continuous ventilation;
7) Minimum maintenance;
8) Two years guarantee.
(1) Italian translation, source: ISHS Tonini F. e E. Remini (24/08/1997)
©2004 - Domenico Brancato snc - All rights reserved - privacy